1. Introduction to Thermal Oil: Analysis of Physical and Chemical Properties
Thermal oil (also known as heat transfer fluid or heat carrier oil) is an organic or synthetic oil used for heat transfer in industrial heating systems. It offers excellent thermal conductivity and stability, allowing long-term operation at high temperatures without significant degradation.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Thermal Oil
- High Boiling Point: Typically exceeds 300°C at atmospheric pressure, making it suitable for high-temperature heating systems.
- Low Freezing Point: Maintains fluidity even in low-temperature environments, facilitating system startup.
- High Thermal Stability: Resists oxidation and cracking at high temperatures, extending service life.
- Excellent Thermal Conductivity: Efficiently transfers heat with minimal energy loss.
- Low Toxicity: Most synthetic thermal oils pose minimal harm to humans and the environment.
Thermal oils are mainly categorized into mineral-based and synthetic types, with synthetic oils (e.g., alkylbenzenes, hydrogenated terphenyls) offering superior thermal stability and longer service life.
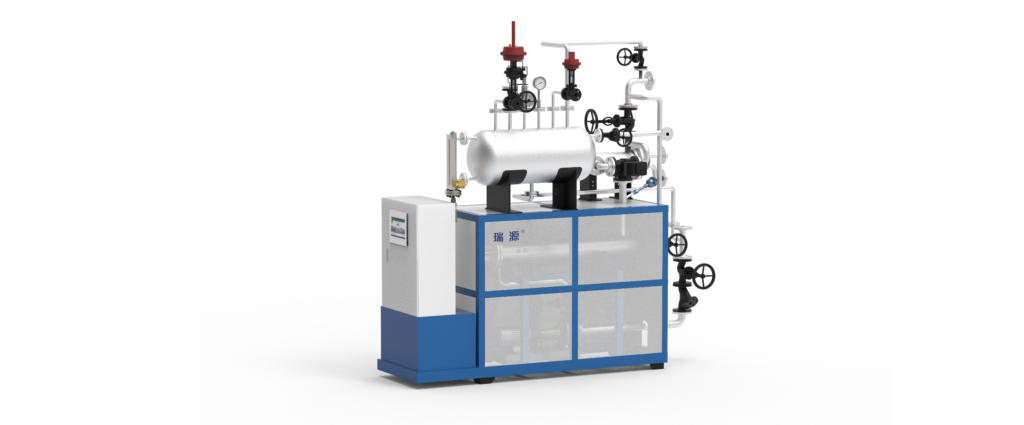
2. Structure of Electric Heating Thermal Oil Heaters: Key Components Explained
An electric heating thermal oil heater consists of the following key components:
- Electric Heating Elements
- Typically made of stainless steel or alloy resistance heating rods, immersed directly in the thermal oil.
- High power density enables rapid heating.
- Heater Body (Oil Tank)
- Constructed from high-temperature and pressure-resistant steel, containing the thermal oil.
- Equipped with insulation layers to minimize heat loss.
- Circulation Pump
- Forces the thermal oil to circulate, ensuring even heat distribution to the target equipment.
- Control System
- Includes temperature sensors, PLC, or PID controllers for precise temperature regulation.
- Features safety functions such as over-temperature protection and low-level alarms.
- Expansion Tank
- Compensates for thermal oil volume changes due to temperature fluctuations, maintaining stable system pressure.
- Filtration System
- Prevents pipeline clogging from impurities, prolonging thermal oil lifespan.
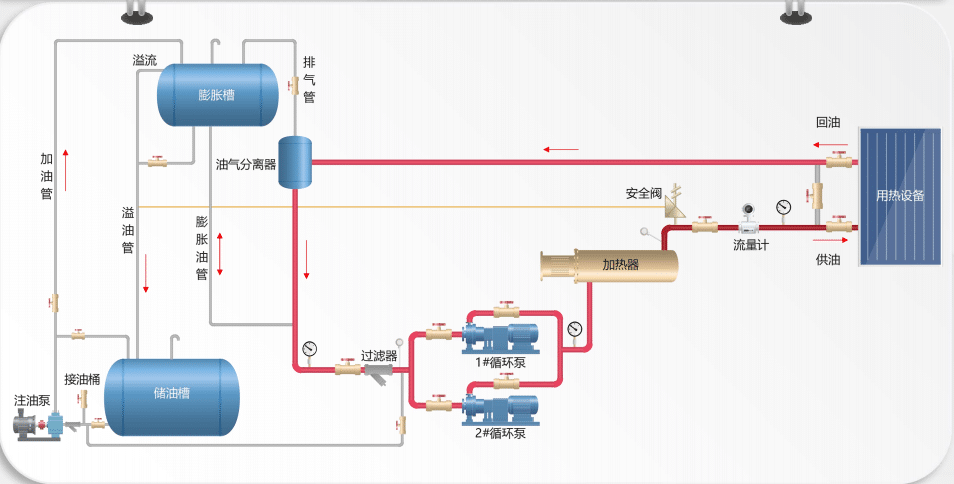
3. Working Principle of Electric Heating Thermal Oil Heaters: Heat Transfer Process Explained
The operational process of an electric heating thermal oil heater is as follows:
- Heating Phase: Electric heating elements generate heat when powered, transferring it to the thermal oil to raise its temperature.
- Circulation Phase: The circulation pump drives the high-temperature thermal oil through heat-consuming equipment (e.g., reactors, dryers), where it releases heat before returning to the heater for reheating.
- Temperature Control: Temperature sensors monitor the oil temperature in real-time, while the control system adjusts heating power to maintain the set temperature accurately.
This closed-loop cycle ensures high thermal efficiency and precise temperature control.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Heating Thermal Oil Heaters
Advantages
- High Energy Efficiency: Achieves over 98% electric-to-heat conversion efficiency, outperforming coal or gas heating methods.
- Eco-Friendly: No combustion emissions, complying with environmental regulations.
- Precise Temperature Control: PID-controlled systems maintain temperature within ±1°C.
- Safe and Reliable: No open flames or high-pressure steam, reducing explosion and leakage risks.
- Compact Design: Small footprint, easy installation, suitable for diverse industrial applications.
Disadvantages
- Higher Operating Costs: Electricity costs may exceed those of gas or coal systems, though optimized heating strategies can reduce consumption.
- Thermal Oil Degradation: Prolonged high-temperature operation may cause oil aging, requiring periodic testing and replacement.
- Higher Initial Investment: Premium electric heating systems and thermal oils involve higher upfront costs but lower long-term maintenance expenses.
5. Applications of Electric Heating Thermal Oil Heaters: Suitable Industries
Electric heating thermal oil heaters are widely used in:
- Chemical Industry: Reactor heating, distillation, polymerization.
- Plastics Processing: Temperature control for injection molding and extrusion machines.
- Food Industry: Edible oil processing, baking equipment.
- Textile and Dyeing: Fabric drying and shaping.
6. Conclusion: Why Choose an Electric Heating Thermal Oil Heater?
With advantages such as high efficiency, environmental friendliness, and precise temperature control, electric heating thermal oil heaters https://8ruiyan.com/en/all-organic-heat-carrier-boilers/are an ideal choice for modern industrial heating. Despite higher initial costs, their long-term stability and low maintenance make them a preferred solution across industries. Selecting the right thermal oil and optimizing system design can further enhance performance and cost-effectiveness.
If you seek a clean, efficient heating solution, an electric heating thermal oil heater is undoubtedly worth considering!
For technical inquiries, contact Ruiyuan’s official support team!
📞 📞 📞
Whatsapp:86-19106101570
wechat:86-19106101570
email:nieyili@cnryan.com
