Important Design Features of Thermal Oil Boilers
Thermal oil boilers are designed for efficient heat transfer in industrial settings, using a liquid medium instead of steam or hot water. These boilers are vital for industries that need precise temperature regulation and high heat output.

Closed-Loop Systems
A closed-loop system is central to thermal oil boilers. In this design, thermal oil circulates through the system, picks up heat, and transfers it to processes like heating, drying, and chemical reactions. This system runs at low pressure, making it safer than steam-based systems that require high pressures for similar temperatures. It also minimizes leaks, overheating, and ensures even heat distribution.
Oil Pumping and Flow Design
The flow rate of thermal oil is a crucial design aspect. Proper oil circulation is essential to maintain uniform temperatures across the system. The size, placement, and flow rate of pumps are optimized for effective heat transfer. Larger systems may use multi-stage or booster pumps to maintain proper flow.
Expansion Tanks
Thermal oil expands when heated, and expansion tanks are used to accommodate this increased volume. This helps avoid stress on the system’s pipes and components. The tanks control temperature fluctuations and maintain consistent pressure throughout the system.
Heat Recovery Systems
Heat recovery plays a significant role in enhancing thermal oil boiler efficiency. Economizers and heat exchangers are used to recover waste heat from flue gases. This pre-heats the oil or combustion air, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
Burner and Combustion Control
The burner provides the heat needed for the system, and its design is crucial for efficiency. Burners are tailored for specific fuels, such as natural gas, diesel, or biomass. Advanced control systems ensure optimal air-to-fuel ratios, improving combustion efficiency and minimizing pollutants like NOx and CO2.
What Is the Efficiency of Thermal Oil Boilers?
Boiler efficiency is critical for reducing operational costs and minimizing environmental impact. It can be calculated and improved by focusing on combustion efficiency, heat transfer efficiency, and reducing thermal losses.
Ways to Calculate and Improve Efficiency in Thermal Oil Boilers
Combustion Efficiency
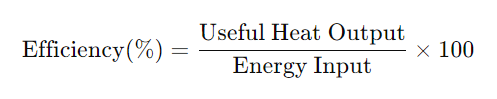
This is the ratio of useful heat output to the energy input from fuel. Efficient combustion results in complete fuel usage, reducing waste. Excess air can improve combustion but may lower efficiency due to increased heat loss with exhaust gases.
Heat Transfer Efficiency
The efficiency of heat transfer depends on factors such as thermal oil properties, pump size, and flow rate. Properly designed heat exchangers and controlled oil circulation are critical for minimizing energy loss.
Thermal Losses
Thermal oil boiler efficiency is impacted by radiation losses from the boiler surface, heat lost through exhaust gases, and losses in pipes. High-quality insulation and heat recovery systems help minimize these losses.
Overall Boiler Efficiency
The overall efficiency is determined by comparing the total energy used to generate heat with the energy provided by the fuel. A well-maintained system can achieve efficiencies of 90% or higher.
Impact of Insulation
Good insulation reduces heat loss from the boiler and system pipes, improving overall thermal efficiency. Advanced insulation materials help retain heat, reducing the need for additional energy inputs.
Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular maintenance and monitoring are essential to sustain high efficiency. By tracking real-time data like temperature, pressure, and fuel consumption, systems can detect inefficiencies early. Maintaining key components, like the burner and heat exchanger, helps prolong the system’s life and ensures peak performance.
Thermal oil boilers are essential in industrial heating systems. By optimizing combustion, minimizing thermal losses, and maintaining key components, you can achieve high efficiency and low operational costs. Continued advancements in design and technology are driving better performance in industrial thermal oil boilers.
Reading:
