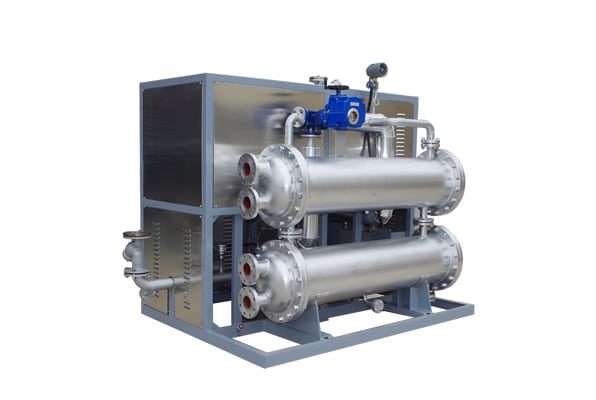
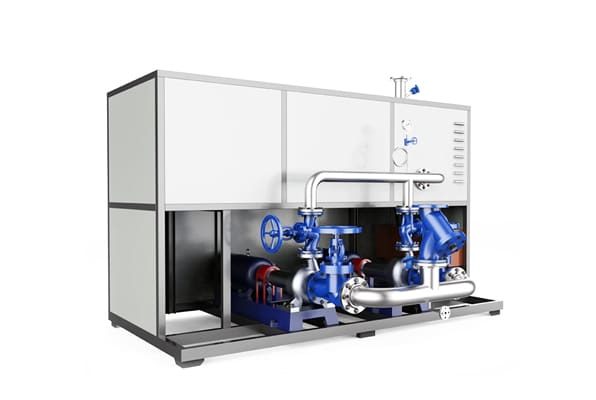
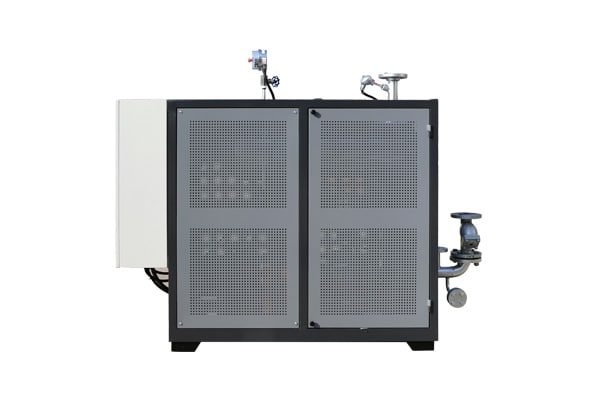
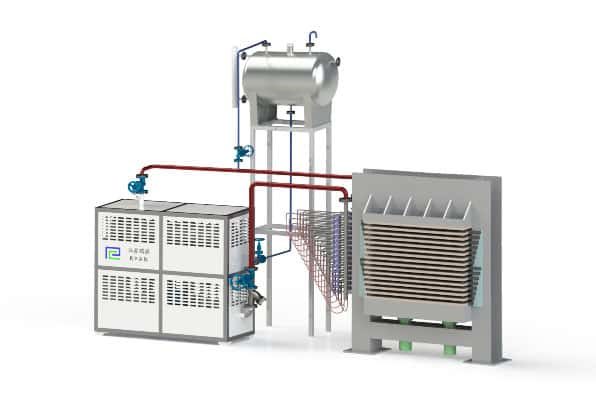
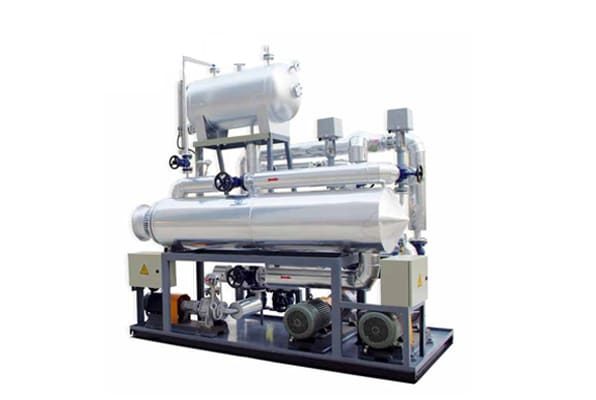
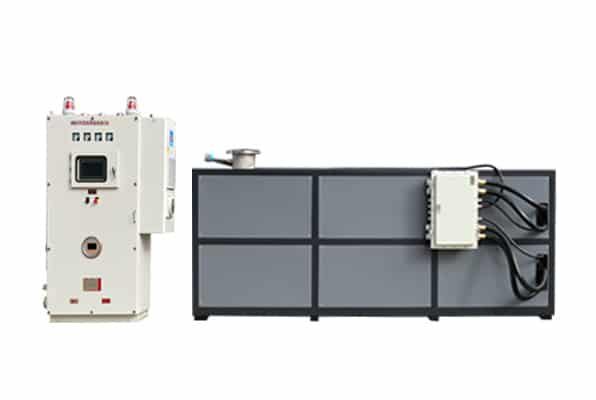
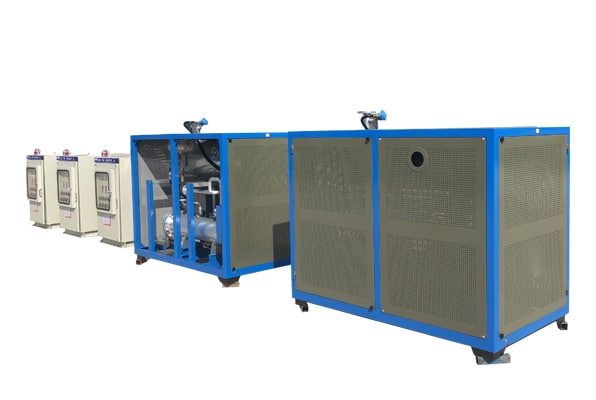
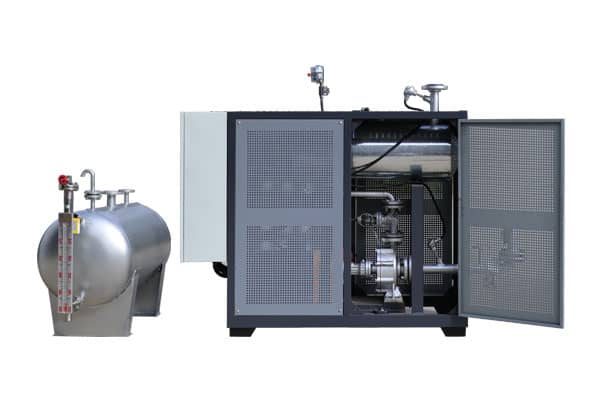
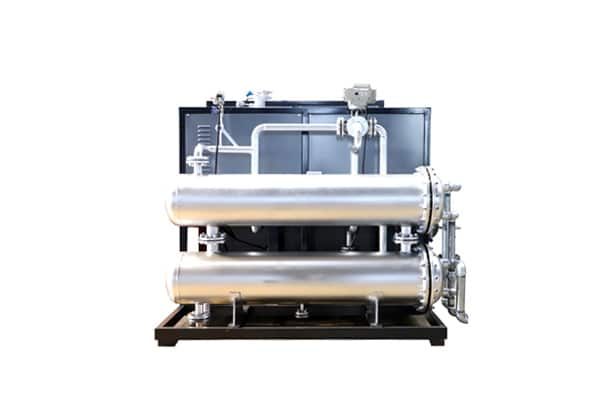
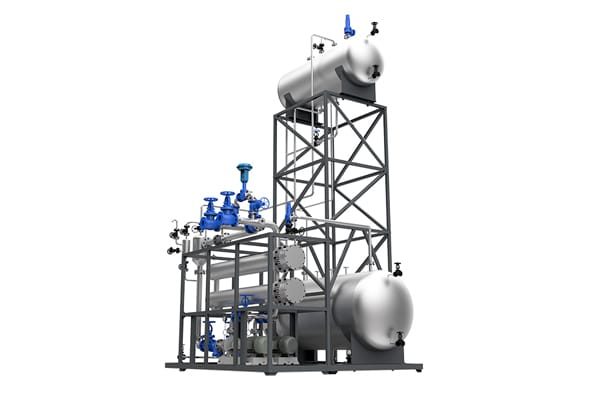
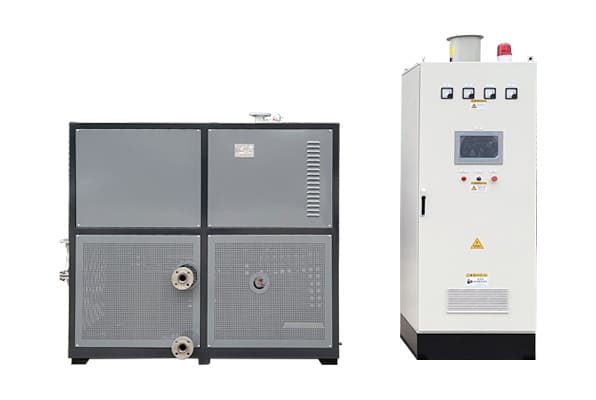
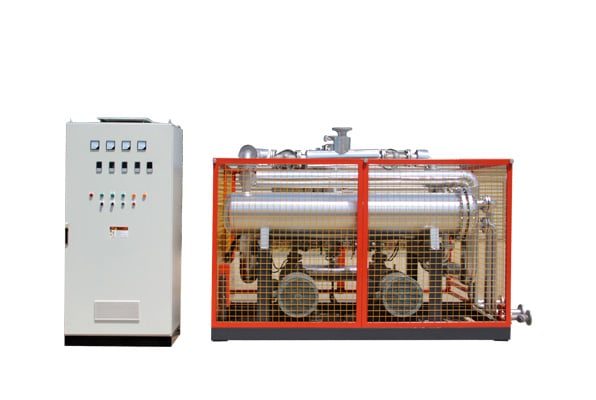
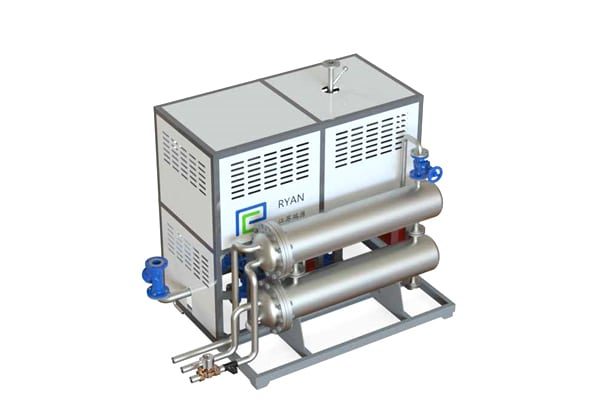
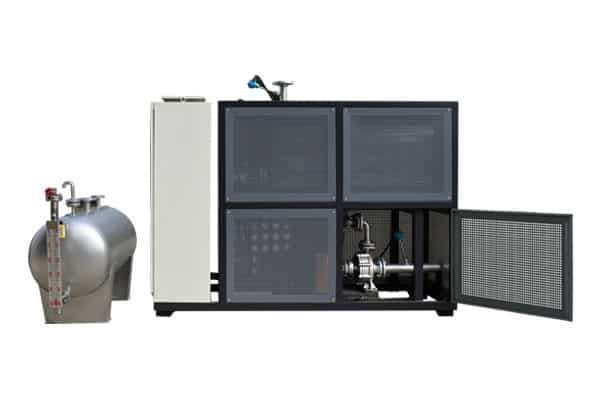
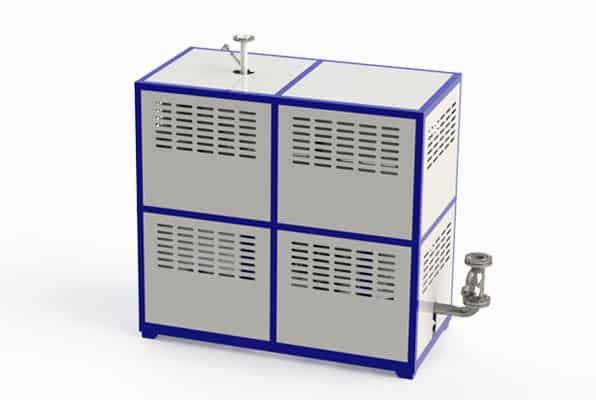
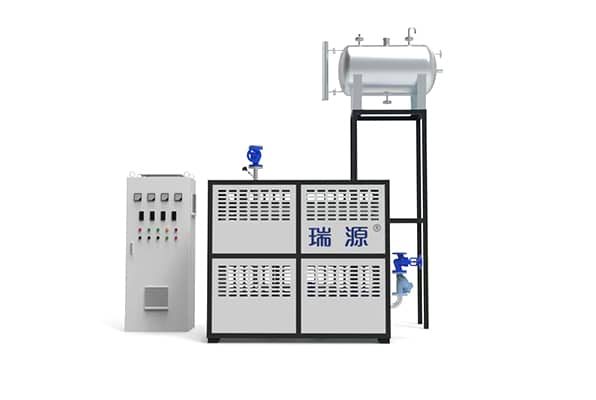
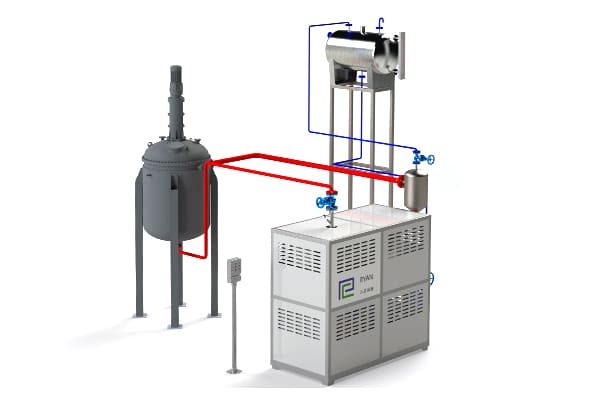
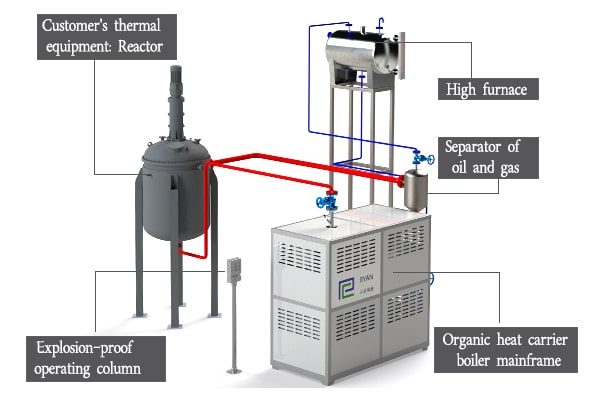
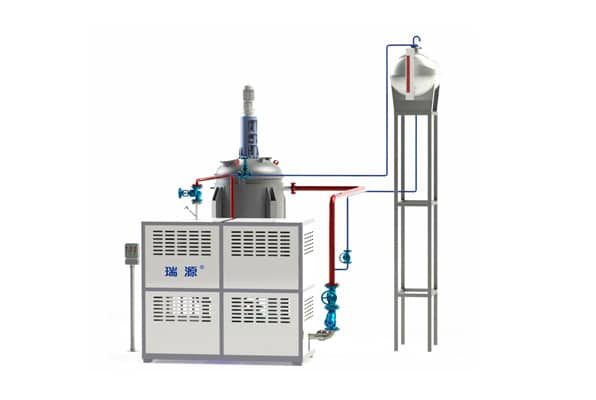
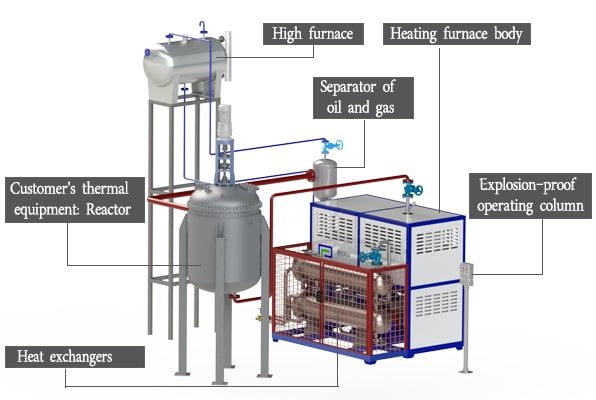
Electrically Heated Thermal Oil Boiler
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
High thermal efficiency-Precise temperature control-Non-standard customisation
The Comprehensive Guide to Thermal Oil Boilers
1. Introduction to Thermal Oil Boilers
1.1 Definition and Overview
Thermal oil boilers, also known as thermal fluid heaters, are specialized heating systems that utilize thermal oil as a heat transfer medium. Unlike traditional steam boilers that rely on water, thermal oil boilers operate at lower pressures while achieving higher temperatures, making them ideal for various industrial applications. Unlike traditional steam boilers that rely on water, thermal oil boilers operate at lower pressures while achieving higher temperatures, making them ideal for various industrial applications. The thermal oil circulates through the system, absorbing heat from the combustion process and transferring it to the desired application.
1.2 Importance in Industrial Applications
Thermal oil boilers play a crucial role in industries that require consistent and high-temperature heating. They are widely used in sectors such as They are widely used in sectors such as chemical processing, food production, and oil refining, where precise temperature control is essential. Their ability to operate at high temperatures without the risks associated with high-pressure steam systems makes them a preferred choice for many industrial applications.
2. Working Principle of Thermal Oil Boilers
2.1 How Thermal Oil Boilers Operate
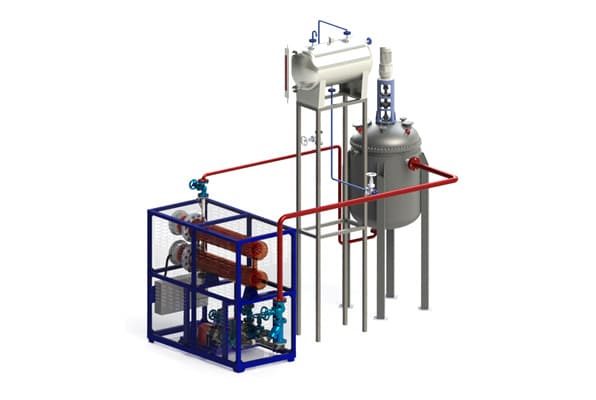
The working principle of thermal oil boilers is relatively straightforward. The system consists of a furnace where fuel is burned to produce hot gases. These gases pass through a series of coils that contain the thermal oil. As the hot gases flow around the coils, they transfer heat to the thermal oil, which As the hot gases flow around the coils, they transfer heat to the thermal oil, which then circulates through the system to provide heating to various processes.
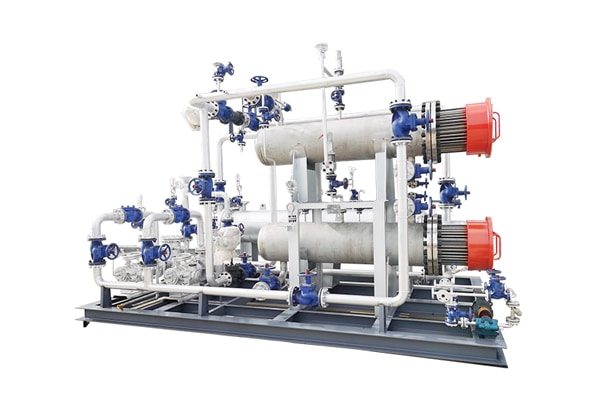
2.2 Components of a Thermal Oil Boiler
Key components of a thermal oil boiler include.
Furnace: The combustion chamber where fuel is burned.
Heating Coils: Tubes that carry thermal oil and absorb heat from the combustion gases.
Burner: Responsible for igniting the fuel and maintaining the combustion process.
Circulation Pump: Moves the thermal oil through the system.
Expansion Tank: Accommodates the thermal expansion of the oil.
3. Comparison: Thermal Oil Boiler vs Steam Boiler
3.1 Key Differences
When comparing thermal oil boilers to steam boilers, several key differences emerge.
Operating Pressure: Thermal oil boilers operate at lower pressures, reducing the risk of explosions and leaks.
Temperature Range: Thermal oil can reach temperatures of up to 600°F (315°C) without boiling, while steam requires high pressure to achieve similar temperatures.
Maintenance: Thermal oil systems generally require less maintenance due to the absence of scale formation and corrosion common in steam systems.
3.2 Advantages of Thermal Oil Boilers
The advantages of thermal oil boilers include.
Enhanced Safety:: Lower operating pressures reduce the risk of catastrophic failures.
Cost Efficiency:: Reduced maintenance and operational costs compared to steam boilers.
Longer Lifespan: The absence of corrosion and scale formation leads to a longer service life.
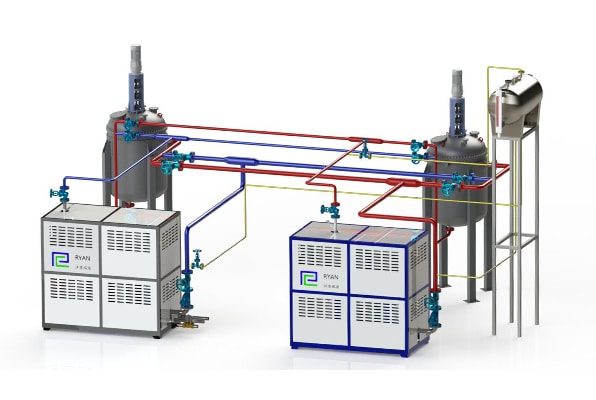
4. Applications of Thermal Oil Boilers
4.1 Use in Ships
Thermal oil boilers are increasingly utilized in marine applications, particularly in ships. They provide efficient heating for various onboard systems, including cargo heating and engine room heating. The ability to operate at lower pressures makes them suitable for the confined spaces of a ship, enhancing safety and reliability. The ability to operate at lower pressures makes them suitable for the confined spaces of a ship, enhancing safety and reliability.
4.2 Industrial Heating Systems
In industrial settings, thermal oil boilers are employed for processes that require consistent and high-temperature heating. Industries such as Industries such as plastics, textiles, and food processing benefit from the precise temperature control offered by thermal oil systems.
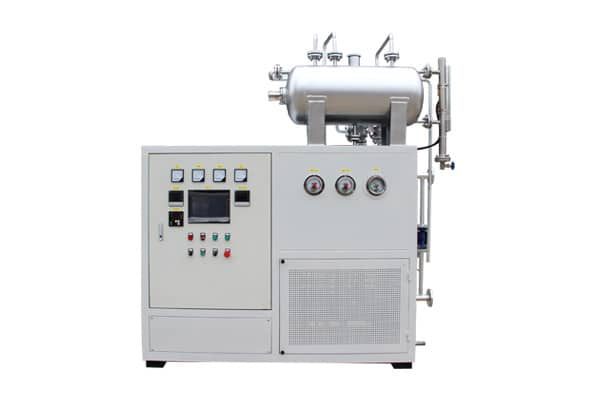
5. Electric Thermal Oil Heaters
5.1 Functionality and Benefits
Electric thermal oil heaters are an alternative to traditional fuel-fired thermal oil boilers. They utilize electric heating elements to heat the thermal oil, providing a clean and efficient heating solution. They utilize electric heating elements to heat the thermal oil, providing a clean and efficient heating solution.
Reduced Emissions: Electric heaters produce no combustion emissions, making them environmentally friendly.
Lower Operating Costs: They can be more cost-effective in areas with low electricity rates.
Ease of Installation:: Electric thermal oil heaters require less infrastructure compared to fuel-fired systems.
6. Maintenance and Safety Considerations
6.1 Common Issues and Solutions
While thermal oil boilers are generally low-maintenance, some common issues can arise, such as.
- Overheating: Regular monitoring of temperature and pressure is essential to prevent overheating.
- Contamination: Ensuring the thermal oil remains uncontaminated is crucial for system efficiency. Regular filtration can help mitigate this issue.
6.2 Safety Precautions
Safety is paramount when operating thermal oil boilers. Key precautions include.
Regular Inspections: Routine checks of all components to ensure proper functioning.
Leak Detection: Implementing systems to detect leaks promptly can prevent environmental damage and safety hazards.
Training:: Ensuring operators are trained in the safe handling and operation of thermal oil systems.
7. Conclusion
7.1 Summary of Benefits
Thermal oil boilers offer numerous advantages, including enhanced safety, lower operating costs, and longer lifespans compared to traditional steam boilers. Their ability to operate at high temperatures without the associated risks of high pressure makes them an ideal choice for various industrial applications. applications.
7.2 Future Trends in Thermal Oil Heating Systems
As industries continue to seek more efficient and environmentally friendly heating solutions, the demand for thermal oil boilers is expected to grow. Innovations in thermal oil technology, including improved materials and automation, will further enhance the efficiency and safety of these systems, solidifying their role in modern industrial heating applications. Innovations in thermal oil technology, including improved materials and automation, will further enhance the efficiency and safety of these systems, solidifying their role in modern industrial heating applications.
In summary, thermal oil boilers represent a versatile and efficient solution for high-temperature heating needs across various industries, including their critical applications in marine environments and industrial heating systems.